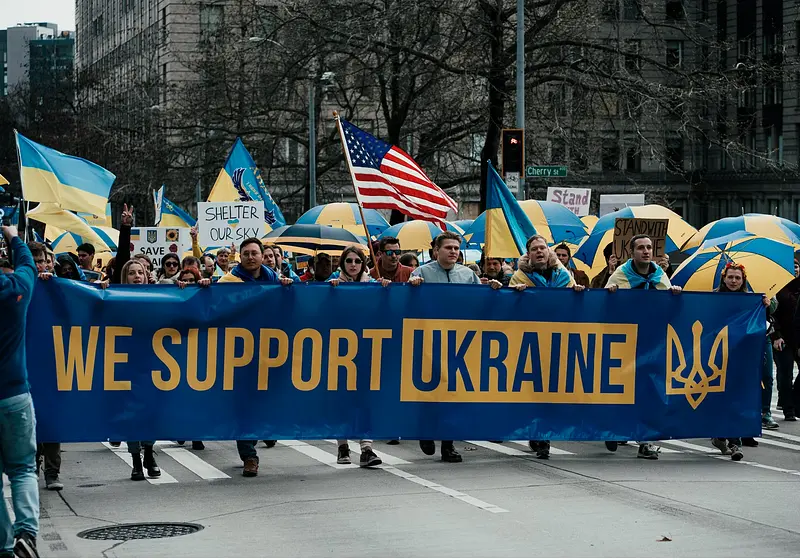
In March, you couldn't go online without being flooded with posts about the Russia-Ukraine crisis, or leave your home without seeing a Ukraine flag. This performative activism didn't last long, though, and most people are likely to have taken limited action because they believe they aren't affected or aren't educated on the severity of the crisis. However, the effects of western sanctions on Russia are seen throughout the world.
Let us slide into your dms 🥰
Get notified of top trending articles like this one every week! (we won't spam you)Background: Russia-Ukraine Crisis
From 1922 to 1991, Russia, Ukraine, and thirteen other republics comprised the Soviet Union. It was extremely influential until its final years when it collapsed because Russia, its main source of power, could no longer afford the military and other expenses. Many of the countries within it, including Ukraine, became independent. Some countries joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) for security, which includes prosperous western countries like the United States and Canada.
Since the Soviet Union fell apart, NATO has been prospering, which Putin claims ruined Russia and Ukraine's "historic future as a nation." While Ukraine is not a part of NATO, it has been receiving military assistance and other resources from NATO countries since Russia invaded the Ukrainian peninsula, Crimea, in 2014.
In February 2022, Russia launched the largest invasion yet into Ukraine, causing the biggest refugee crisis in Europe since World War II.
Stephanie Von Hlatky, the Canada Research Chair on Gender, Security, and the Armed Forces, believes this attack was to distract Russians from the problems their country is facing as Putin's career comes to an end.
Dmytro Kuleba, Ukraine's minister of foreign affairs, requested help and gained the support of nearly every country through sanctions.
Take the Quiz: Which Indian city is the perfect holiday spot for you!?
Let's match you with an Indian city that you would love!
Sanctions on Russia
Sanctions are penalties that limit a country's abilities, usually created by one country to reduce the power of another. To help Ukraine, NATO countries have imposed sanctions on Russia.
The United States banned all Russian oil and gas imports, and the United Kingdom will ban all Russian oil imports by the end of 2022. The European Union will ban Russian coal imports by August 2022, and Germany stopped progress on a major gas pipeline from Russia. The 7 biggest Russian banks have been removed from S.W.I.F.T. (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication), and the United Kingdom removed and froze major Russian banks in the U.K financial system. More than 1,000 wealthy Russians have been sanctioned by the United States, the European Union, and the United Kingdom, including oligarchs and government officials.
However, Putin was prepared and fought back. Russia banned the exports of over 200 products and stopped paying foreign investors and shareholders, banning those with Russian investments worth billions of dollars from selling them.
Sanctions: Pros and Cons
Sanctions on Russia have not only caused the country to face delays in payments for exports, but it does not have the money to pay back loans and is in debt. Russia's economy is predicted to be reduced by 10% in 2022, with a deep recession looking likely. The country will no longer be able to afford war expenses, and many experts anticipate it will pull back troops.
While the sanctions have limited Russia, they don't adequately address the damage that has already happened.
“Sanctions are an important tool but no panacea. They can and will increase the cost to Russia of Putin’s war, and they may well contribute to public disaffection in Russia, but for now what will matter most is what happens on the ground in Ukraine.”
-Richard Haass, President of the Council on Foreign Relations
This does not only affect Russia and Ukraine. Russia is a large exporter of wheat, petrol, and oil, among others, so because of the disruption in the global supply chain from the sanctions, you can expect to see already-high prices continue to skyrocket, and further product shortages. Europe is extremely reliant on energy from Russia, so the sanctions will cause the continent to struggle significantly.
The U.S., though, can easily find a replacement source of energy. In 2021, Russia made up 26 percent of European petroleum and gas imports, but only 8 percent of the U.S's imports.
Final Thoughts
In support of Ukraine, NATO countries have imposed sanctions on Russia to limit its power. While it has caused the Russian economy to suffer, millions of Ukrainians are displaced and are receiving inadequate support. Countries are seeing surges in prices, and in combination with product shortages, many people are struggling to afford necessities.
Sanctions on Russia have had a variety of effects on the world, good and bad. We must educate ourselves and others about the global effects of sanctions to create further, genuine action.